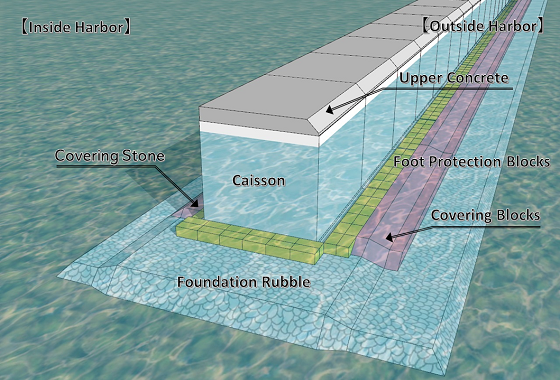
A caisson is a large box made of reinforced concrete. It is used as a breakwater to prevent waves and a quay to anchor ships.
Outline of Caisson Quay and Breakwater Construction Technology
Caisson quay and breakwater construction is generally carried out in the order of foundation work, main work, covering work and foot protection work, and superstructure work.
Recent advances in construction and ICT technologies have made it possible to construct buildings efficiently, accurately, and safely.
-
Foundation work
Stone materials carried in by GATT vessels are offloaded at the construction site, and then divers flatten the uneven ocean bed.
Our technology:With the advent of underwater backhoes and giant tamper construction methods, it has become possible to mechanically move rubble, work that divers used to conduct manually. -
Installation Work
This process involves lifting the created caisson to the surface and, by using a crane ship, etc., placinge the caisson on a rubble foundation.
Our technology:This process is benefitted by our construction support system, which automatically controls the installation posture of the caisson.
-
Covering and Foot Protection Work
Covering and foot protection blocks are placed over the foundation rubble.
These work to prevent the foundation rubble, which forms the foundation of breakwaters, from being scraped off or washed away by the force of strong waves.
Our technology:The crane used to install the blocks can be equipped with an installation support system (block installation support system) to ensure efficient installation. -
Superstructure Work
 Caisson Breakwater
Caisson Breakwater
About Caissons
Caisson is French for “a large box”. A caisson is a box made out of steel-reinforced concrete that is used as a breakwater to prevent waves and as a quay to anchor ships.
In ports, caissons are used in a variety of ways, including as breakwaters, quays, and as bridge foundations. Caissons used as breakwaters vary in size, ranging from 500 tons to 10,000 tons, with larger caissons typically used in locations with stronger waves.
A Caisson can be created on land at a caisson yard or on a special platform ship called a floating dock.
A completed caisson has the shape of an empty box consisting of numerous square sections. This shape allows the caisson to float on the ocean surface and be towed by a boat to the installation site where it is then sunk and installed.
Construction Flow
1.Foundation Work (Investing and Leveling of Foundation Rubble)
Foundation work is conducted so the caisson can be installed at the construction location.
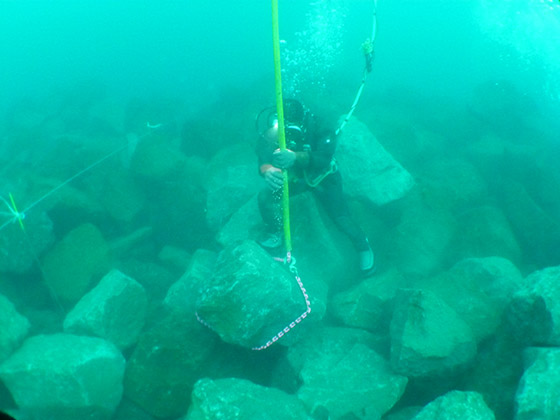
Stone materials transported via a GATT vessel are offloaded at the installation site, after which divers flatten the uneven ocean bed.
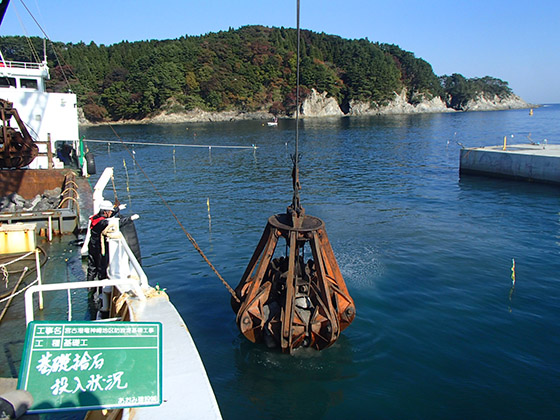 Foundation rubble offloading
Foundation rubble offloading
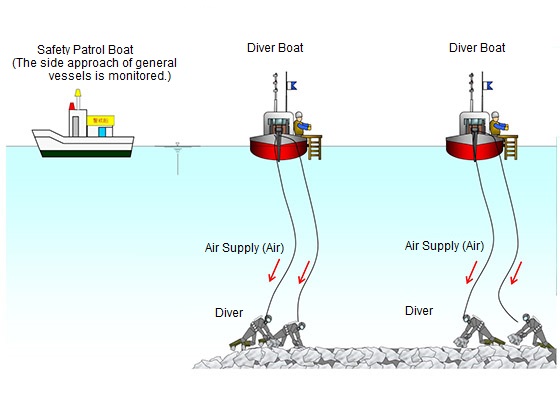 Divers conducting flattening work
Divers conducting flattening work
 Heavy objects are moved using a diver boat's winch
Heavy objects are moved using a diver boat's winch
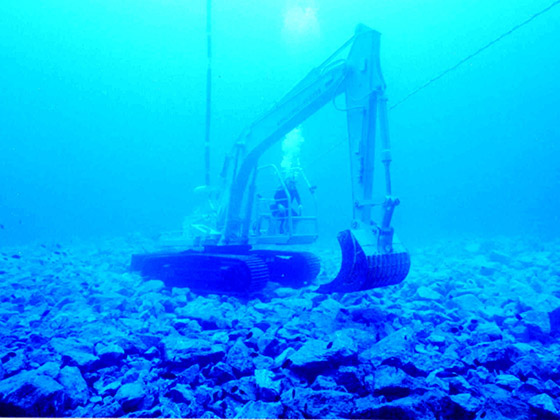 Flattening work using an underwater backhoe and big club
Flattening work using an underwater backhoe and big club
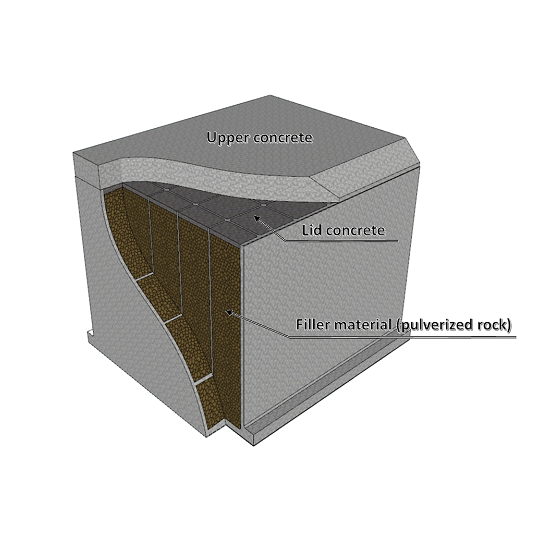
2.Main Work (Caisson Towing, Installation, Filling and Placing Lid Concrete)
The caisson positioned in the harbor is floated and towed to the installation site, where it is sunk and installed.
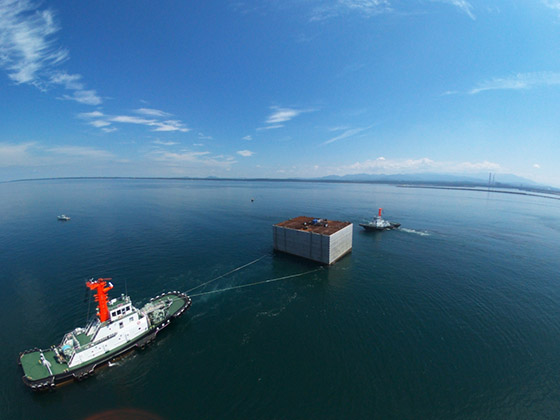 Caisson towing
Caisson towing
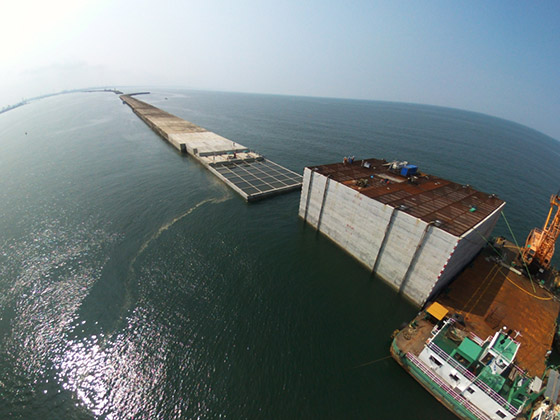 Caisson installation
Caisson installation
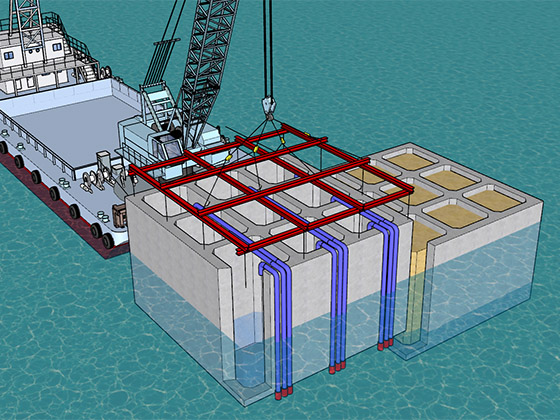 Installation (flooded with water to sink)
Installation (flooded with water to sink)
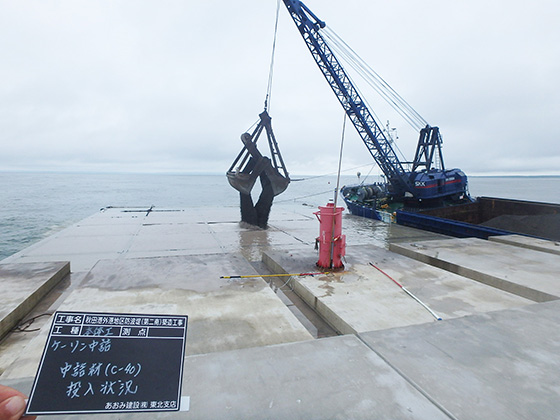 Filler material inserted
Filler material inserted
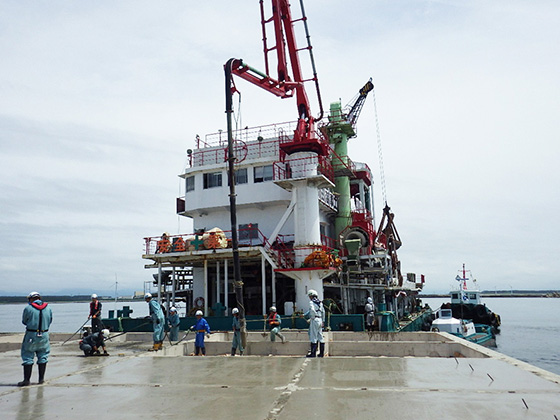 Laying lid concrete
Laying lid concrete
3.Covering and Root Foot Protection Work (Installation of Foot Protection Blocks and Covering Blocks)
.jpg)
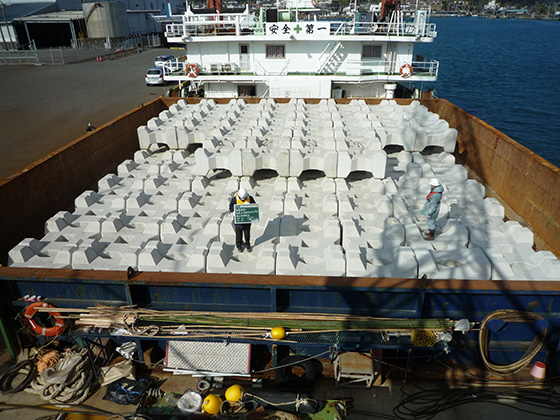 Foot protection blocks loaded on vessel
Foot protection blocks loaded on vessel
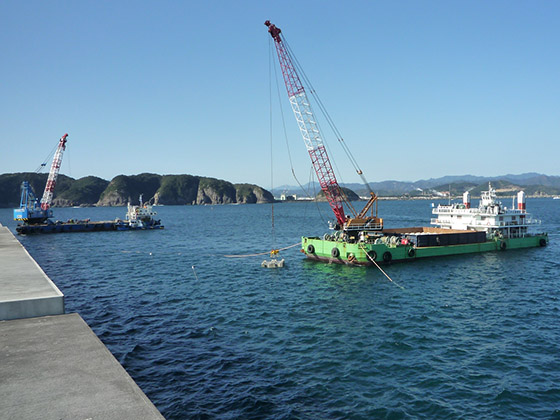 Foot protection block installation work
Foot protection block installation work
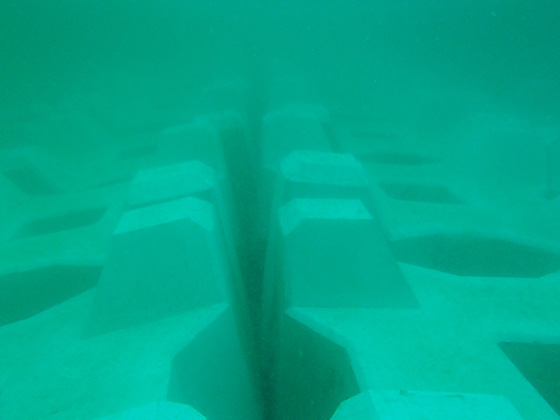 Installed foot protection block
Installed foot protection block
4.Superstructure Work (Form Assembly, Reinforcement Assembly, and Concrete Installation)
Formwork is assembled in the upper part of the installed caisson, and a mixer ship slays the concrete.
.jpg)
Our Technology Used in Construction of Caisson Quays and Breakwaters

Underwater Backhoe Big Crab
This technology mechanizes the screeding work done by divers in the water.
Construction Results

Construction Work on Outer Port of Sakaiminato and Wharf in Nakano District
Sakaiminato City, Tottori Pref

Construction Work of Breakwater (Second South) in Outer port Area of Akita Port
Akita City, Akita Pref


 Contact
Contact Japanese
Japanese